|
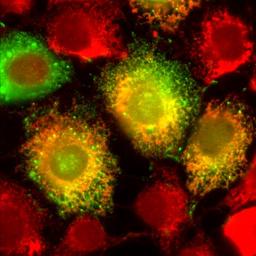
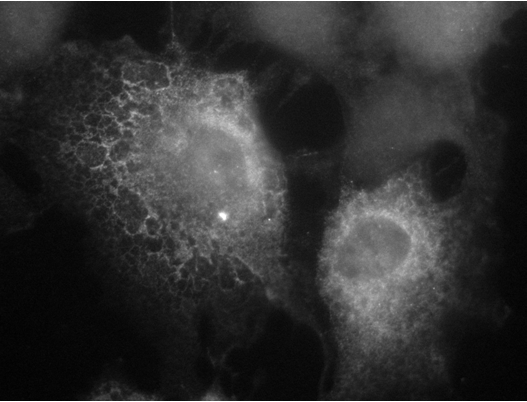
Gene expression plays a critical role in regulating and modifying various cellular functions, which impact on processes such as development and homeostasis. Gene activation begins in the nucleus, where DNA is transcribed into a nascent transcript that is processed so that non-coding introns are removed by the splicesome, and a cap and poly-A tail are added to the beginning and end of the RNA, respectively. Once processing is complete, the mature messenger RNA (mRNA) is exported to the cytoplasm where it localizes to distinct subcellular sites. For example in higher eukaryotes, mRNAs coding for secreted and membrane bound proteins are targeted to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). |
|
Our lab utilizes sophisticated cell manipulation protocols, such as nuclear microinjection, in order to figure out:
|
|
|
